
- CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY HOW TO
- CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY MAC
- CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY WINDOWS
Let’s start off with erasing a volume to casually remove any stored data on the selected volume. We’ll be using the Disk Utility app included with macOS High Sierra and later.
CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY HOW TO
If you’re working with macOS Sierra or earlier, you may find the Rocket Yard Guide: How to Use Mac’s Disk Utility to Securely Wipe a Drive a good source of information for erasing your drives. We’ll be looking at drives formatted with APFS as well as those formatted with the traditional HFS+ file system.

In this guide, we’re going to look at erasing volumes, partitions, and containers.
CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY MAC
The second change that directly affects the Mac community, at least in the way free space can be securely erased, is the release of the APFS file system, and how it makes use of shared space between multiple volumes.
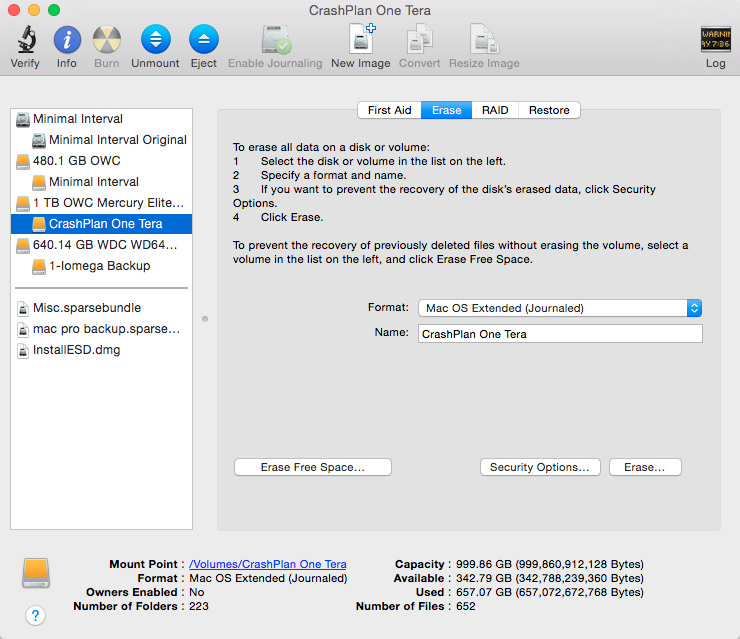
(Using the Security Options to sanitize a volume may be a thing of the past.) The first change, leading to less reliance on the various secure wipe options, has been the proliferation of SSDs, both as original equipment provided by Apple and by resellers, such as OWC, which bring higher performance storage systems to the Mac. Two recent changes have made the traditional secure wipe, performed by overwriting a volume multiple times with various types of data patterns, largely a thing of the past. Even though the default for Disk Utility is a simple erase, a secure wipe was just a few clicks away. Grinding the flash chips to dust prevents recovery but not many other destruction methods are reliable against a well equipped adversary.Securely wiping a drive, removing all of its data, and ensuring that no meaningful information can be recovered, has long been a feature of Disk Utility and its erase function. A similar feature is sometimes implemented by SSD drive manufacturers on specially made security drives that can wipe their disk keys on command. One way is to encrypt the data before you write it, then ensure you never store the key in persistent storage. The strategies for cleaning the disk, then, are limited to ways that don’t involve overwriting. That means even if you use a disk wiping program that overwrites 100% of your disk’s advertised space, some of your data may remain in the over-provisioned areas of the chip. These are called “wear leveling” strategies.
To preserve drive function as long as possible, SSD memory management involves over-provisioning storage by oversizing the flash chips by anywhere up to 20% extra, and using algorithms to spread their writes across different places on the chips. You need to plan in advance if you want to be able to securely delete data from an SSD.īecause flash memory is imperfect, individual bits wear out faster the more often they are used. Until that particular slot is reused or the database is compressed/vacuumed the data is potentially still there. Similar to the MFT, removal of an entry in a database does not deallocate the database file. This is important because when these small files are deleted, only the usage indicator is deleted from the MFT, but the MFT itself is NEVER deallocated. Small files ( in the under 1 KB range but varies) may be stored directly in the Master File Table instead of as their own file.
CANT USE ERASE FREE SPACE DISK UTILITY WINDOWS
The few that could perform the necessary chip off disassembly are rare, very expensive, and still have poor capabilities to reassemble the wear bits into anything coherent.ĭeleting and wiping files in Windows does not necessarily touch previous versions of those files kept by Windows for file recovery. This data is beyond the reach of all standard forensic labs. Once swapped out, the old data in the cell is no longer reachable to be wiped. This is an effect of SSD’s swapping physical storage cells with spares as the cells begin to wear out. That said, there are GOTCHAS to be aware of! If for whatever reason you want to roll your own as it were, you can use any of a myriad of cleaning utilities or simply create a giant file of arbitrary data until you run out of space then delete the file. " NTFS DisableDeleteNotify = 1" Which means TRIM is OFF. " NTFS DisableDeleteNotify = 0" Which means TRIM is ON. To check if TRIM is on in Windows, from a command prompt:įsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify Assuming that the SSD has a properly implemented TRIM function, then Free Space should already be wiped for you, this is what TRIM does as a side effect of preparing deleted/unallocated files for reuse in an SSD.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
